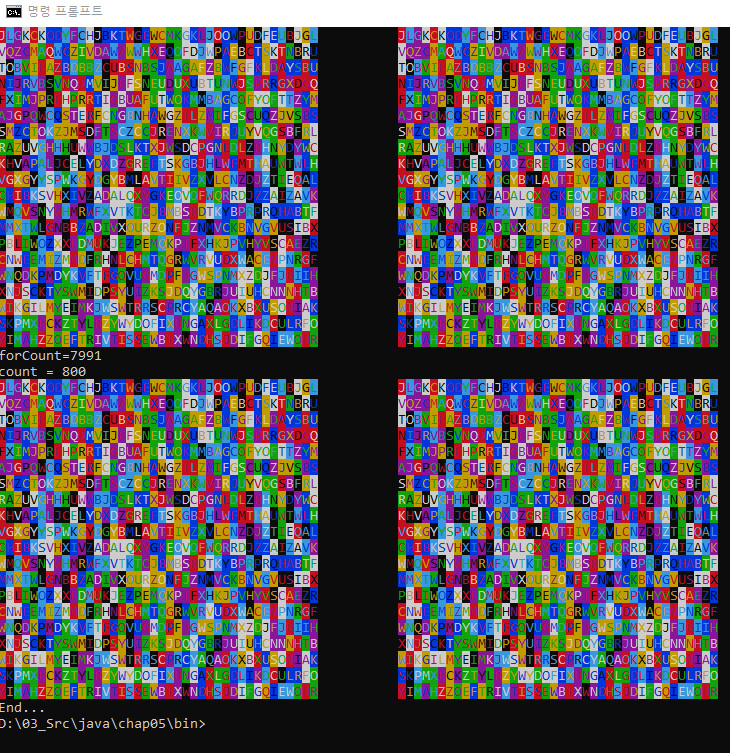
배열로 작성된 코드를 저장하고 복사하여서 4개의 화면을 이어서 출력하도로록 응용.
배열 Array 이론 정리.
배열 Array
- 다차원 배열
new 연산자로 다차원 배열 생성
: new 연산자로 다차원 배열을 생성하려면 배열 변수 선언 시
타입 뒤에 대괄호 [] 를 차원의 수만큼
붙이고, new 타입 뒤에도 차원의 수만큼 대괄호 []를 작성
타입[][] 변수 = new 타입[1차원수][2차원수];
열 1차원
행 열 2차원
면 행 열 3차원
- 객체를 참조하는 배열
배열에서 객체 참조하기
: 기본 타입 Primitive type (byte, char, short, int, long, float, double, boolean)
배열은 각 항목에 값을 직접 저장
: 참조 타입 Reference type (class, interface) 배열은 각 항목에 객체의 번지를 저장
String[] strArray = new String[3];
strArray[0] = "Java";
strArray[1] = "C++";
strArray[2] = "C#";
- 배열 복사
배열 복사하기
: 배열은 한 번 생성하면 길이를 변경할 수 없음.
더 많은 저장 공간이 필요하다면 더 큰 길이의 배열을 새로 만들고
이전 배열로부터 항목들을 복사해야 함.
: System의 arraycopy() 메소드를 이용해 배열 복사 가능
System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
원본 배열 원본 배열 새 배열 새 배열 복사 항목 수
복사 붙여넣기
시작 인덱스 시작 인덱스
- 배열 항목 반복을 위한 향산된 for문
배열 및 컬렉션 처리에 용이한 for 문
: 카운터 변수와 증감식을 사용하지 않고, 항목의 개수만큼
반복한 후 자동의로 for 문을 빠져나감
: for 문이 실행되면 1. 배열에서 가져올 항목이 있을 경우 2. 변수에 항목을 저장,
3. 실행문을 실행
: 다시 반복해서 1. 배열에서 가져올 다음 항목이 존재하면
2. - 3. - 1. 로 진행하고 가저올 다음 항목이 없으면 for 문을 종료
for ( 2. 타입변수 : 1. 배열 ) {
3. 실행문;
}
응용 코드.
public class AlphaExample8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\033[2J"); // Clear Screen
boolean[][] rect = new boolean[20][40]; // false/true
int[][][] saveRect = new int[3][20][40];
int forCount=0;
int count=0;
// 1
for (;;) {
forCount++;
int line = (int)(Math.random()*20 + 1); // [1-20]
int column = (int)(Math.random()*40 + 1); // [1-40]
int fg=0;
int bg=0;
do {
fg = (int)(Math.random()*8 + 30); // [30-37]
bg = (int)(Math.random()*8 + 40); // [40-47]
} while(fg + 10 == bg);
char ch = (char)(Math.random()*26 + 'A'); // [A-Z]
System.out.printf("\033[%d;%dH", line, column);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", fg);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", bg);
System.out.printf("%c", ch);
int li = line - 1;
int ci = column - 1;
saveRect[0][li][ci] = ch;
saveRect[1][li][ci] = fg;
saveRect[2][li][ci] = bg;
if (rect[line-1][column-1] == false) {
rect[line-1][column-1] = true;
count++;
System.out.print("\033[22;1H");
System.out.print("\033[0m");
System.out.printf("count = %03d", count);
}
System.out.printf("\033[21;1H");
System.out.printf("\033[0m");
System.out.printf("forCount=%04d", forCount);
if (count==800)
break;
// Thread.sleep(1);
}
// 2
for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<40; j++) {
int line = i + 1;
int column = j + 1;
char ch = (char)saveRect[0][i][j];
int fg = saveRect[1][i][j];
int bg = saveRect[2][i][j];
System.out.printf("\033[%d;%dH", line, column + 50);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", fg);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", bg);
System.out.printf("%c", ch);
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
// 3
for (int j=0; j<40; j++) {
for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
int line = i + 1;
int column = j + 1;
char ch = (char)saveRect[0][i][j];
int fg = saveRect[1][i][j];
int bg = saveRect[2][i][j];
System.out.printf("\033[%d;%dH", line + 22, column);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", fg);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", bg);
System.out.printf("%c", ch);
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
// 4
for (int j=0; j<40; j++) {
for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
int newi = 19 - i;
int newj = 39 - j;
int line = newi + 1;
int column = newj + 1;
char ch = (char)saveRect[0][newi][newj];
int fg = saveRect[1][newi][newj];
int bg = saveRect[2][newi][newj];
System.out.printf("\033[%d;%dH", line + 22, column + 50);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", fg);
System.out.printf("\033[%dm", bg);
System.out.printf("%c", ch);
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
System.out.print("\033[43;1H");
System.out.print("\033[0m"); // reset
System.out.print("End...");
}
}
'Hello World > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA - 객체 지향 프로그래밍 / 클래스 - 생성자 , 필드, 메소드 / 인스턴스 [개발스터디 기몬] (0) | 2023.03.23 |
|---|---|
| JAVA - 배열 Array [개발스터디 기몬] (0) | 2023.03.10 |
| JAVA - Alpha 랜덤 값 _ 조건문_반복문_배열을 사용해서 명령크롬프트에 화면 출력해보기 (VT100명령어 사용) [개발스터디 기몬] (0) | 2023.03.09 |
| JAVA - 참조타입 Reference type / 기본타입 Primitive type / 배열 Array [개발스터디 기몬] (0) | 2023.03.09 |
| JAVA - 조건문과 반복문을 사용한 EpochTime 현재 날짜, 시간 출력 [개발스터디 기몬] (0) | 2023.03.09 |

댓글